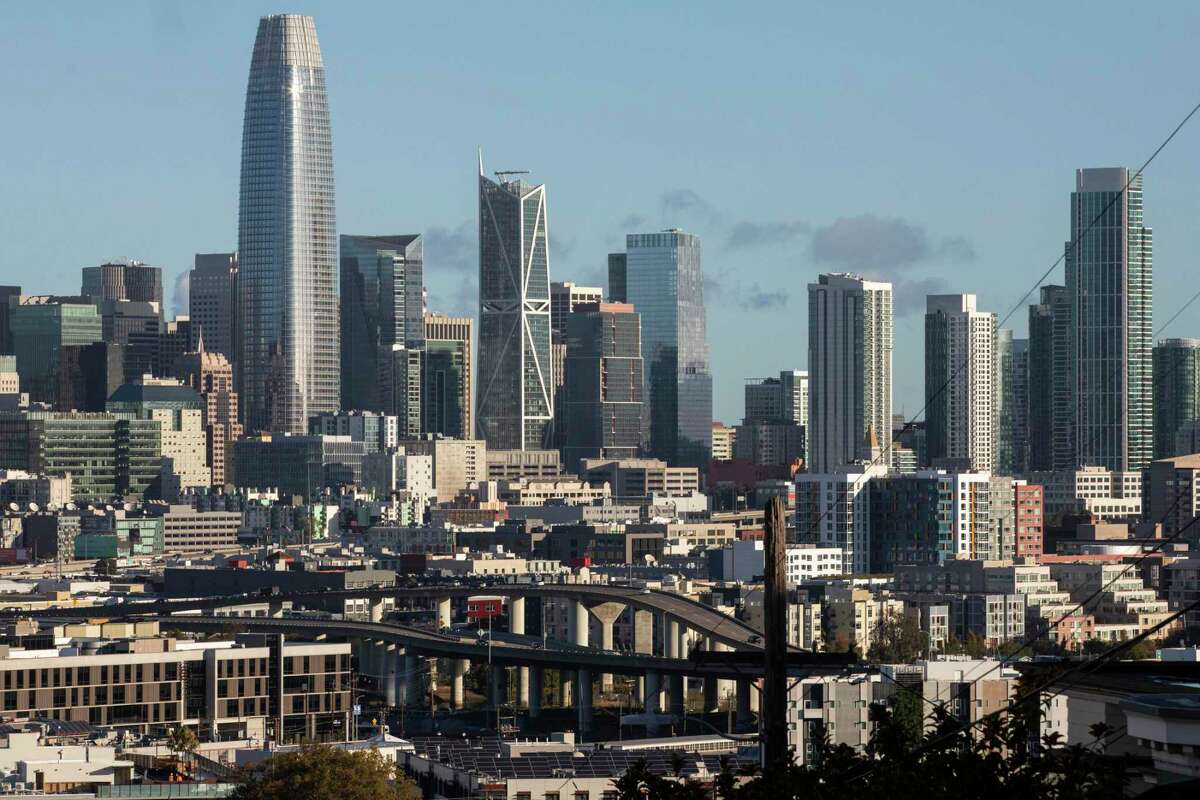
San Francisco’s economic rating dropped sharply during the pandemic, according to a new Brookings Institution report. The region saw a 6.3% loss in jobs in the first two years of the pandemic.
Jessica Christian/The Chronicle 2021The San Francisco metro area saw an economic decline during the early pandemic that was one of the most dramatic in the country, according to anew analysis by the Brookings Institution.
The think tank ranked 192 U.S. metro areas on “inclusive growth,” using a dozen indicators including gross domestic product output, job growth, average wages and the poverty gap.
Between 2011 and 2019, the San Francisco region, which includes the East Bay, ranked fourth overall on inclusive growth. But the region tumbled to 109th based on data between 2019 and 2021, reflecting the pandemic’s toll on the job market and new businesses amid some of the strictest health measures in the country and a widespread shift to remote work.
“While the San Francisco metro area sustained relatively high GDP growth throughout the pandemic, it continued to post losses in overall employment and total jobs at firms (that were) 0-5 years old through 2021,” Joseph Parilla, director of applied research at Brookings Metro, said in a statement.
The region saw a 6.3% loss in jobs and 3.4 percentage point decline in employment rate in the first two years of the pandemic. The unemployment rate has declined since then throughout the Bay Area, though labor force participation has also dropped as some people have chosen not to look for jobs.
“In addition, San Francisco performed worse across the board on overall inclusion indicators (employment rate, median earnings, and relative income poverty rate) from 2019-2021 than they did in the pre-pandemic period,” he said.
圣何塞市区有包容性增长th rate between 2011 and 2019 and fell to 72nd overall during the pandemic. The Silicon Valley area saw a 4% drop in jobs and a 2.6 percentage point decline in employment rate between 2019 and 2021, and much of the western region also saw its rankings drop during the same periods. Seattle, another major tech hub, dropped from third to 97th. Los Angeles fell from 34th to 165th, and Denver dropped from eighth to 121st.
The nation’s biggest metro areas with populations over 1 million saw greater relative losses in jobs compared to smaller areas, according to Brookings. In some cases, less populated areas adjacent to larger metro areas appeared to benefit from a shift in growth trends, including Fresno and Sacramento.
The Brookings study follows other research that concluded San Francisco’s recovery has been among the worst in the country. A University of Toronto and UC Berkeley analysis of cell phone data said downtown San Francisco’srecovery was the weakestamong 62 North American cities as of November 2022.
In the first year of the pandemic, San Francisco saw a6.3% drop in population,the highest percentage of any U.S. city, and the rest of the Bay Area also saw sharp declines.
Reach Roland Li: roland.li@sfchronicle.com; Twitter: @rolandlisf